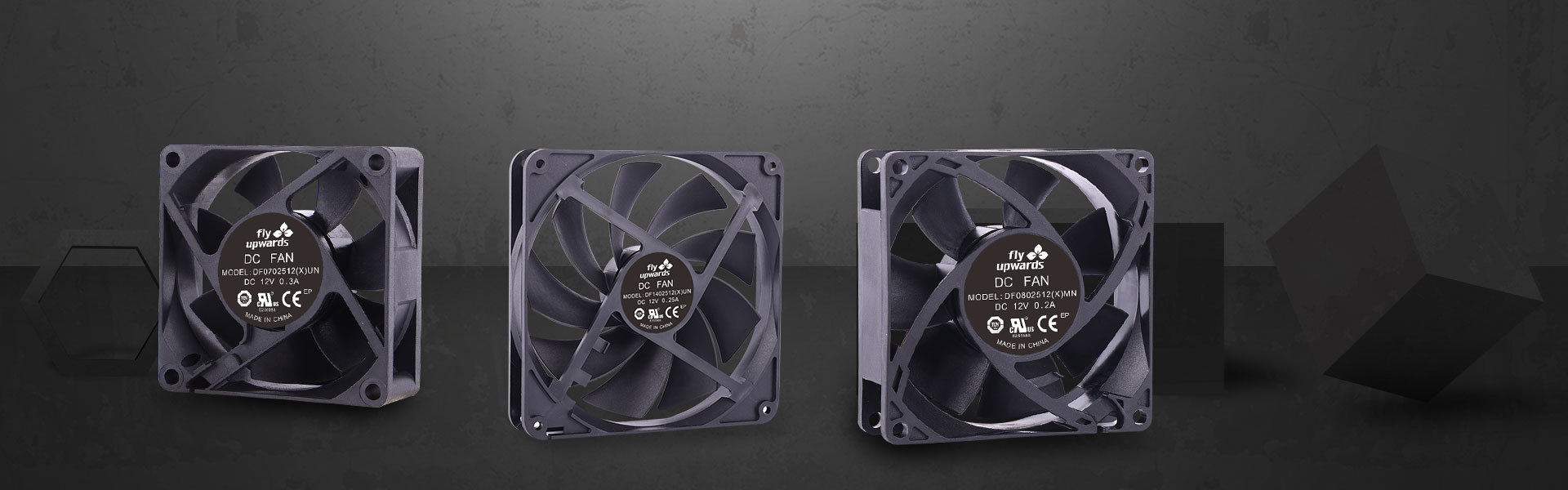
What is DC Fan?
2024-04-20
DC Fan belongs to the field of heat dissipation fans and is one of the most common types of direct current fans. In the fan industry, heat dissipation fans are mainly divided into two types: direct current fans and alternating current fans. Among them, the abbreviation for alternating current fan is AC Fan, while the abbreviation for direct current fan is DC Fan. These two types of fans are among the most common in the fan industry. The main purpose of DC Fan is to provide heat dissipation for electronic devices, and its application scope is very wide. Household appliances such as refrigerators, freezers, air conditioners, etc., all use DC Fan.
Principle of Operation of DC Fan:
The operation principle of DC Fan is based on Ampère's right-hand rule. When a conductor passes through a current, a magnetic field is generated around it. If this conductor is placed in another fixed magnetic field, it will generate attraction or repulsion force, causing the object to move. Inside the blades of a direct current fan, there is mainly a rotor part, on which is attached a pre-magnetized rubber magnet, surrounded by silicon steel sheets. Two sets of coils are wound around the silicon steel sheets, and a Hall sensor component is used as the main stator part of the synchronous detection device to control a set of circuits. This circuit makes the two sets of coils work alternately, generating different magnetic poles. These magnetic poles will produce attraction or repulsion force with the rubber magnet. When this attraction or repulsion force is greater than the static friction force of the fan, the blades will naturally start to rotate. Because the Hall sensor component provides a synchronous signal, the blades can continue to rotate. As for the direction of rotation of the fan, it can be determined according to Fleming's right-hand rule.
By understanding the operating principle of DC Fan, we can better understand its role in the heat dissipation of electronic devices, and how it is applied in various household appliances.